Link G4X ECUs are capable of OBD (On Board Diagnostics ISO 15765) communication using the ECUs CAN module.
OBD data is able to be used by scan tools, and is also capable of being transmitted to a tablet or cellphone using an OBD to bluetooth or wifi device.
Setting up OBD
There are two parts to setting up OBD, the first part is wiring the OBD-II Port to the ECU. The second part is setting up the ECUs CAN bus module, follow the steps below to setup the CAN bus module:
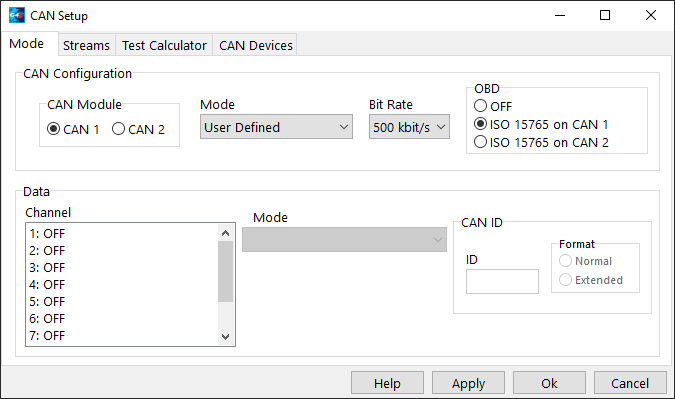
1.Start PCLink and connect (F3 key) to the ECU. Then click ECU Controls > CAN Setup.
2.Select the CAN Module the OBD-II Port has been wired to. Note that some ECUs only have the CAN 1 module available.
3.Set the Mode to any mode other than OFF. If the CAN module is only wired to the OBD-II Port then select 'User Defined'.
4.Set the Bit Rate, most OBD-II scan tools communicate at 250 or 500 kbit/s.
5.Next select either 'ISO 15764-4 on CAN 1' or 'ISO 15764-4 on CAN 2' depending on the CAN Module being used.
6.Click Apply and OK, remember to do a Store of the ECUs base map (F4 key).
If problems are encountered during setup refer to User CAN Setup for more information on CAN Bus configuration.
OBD Data
Currently the following OBD PIDs are supported:
PID Number (Hex) |
PID Number (Dec) |
Description |
PID01 |
PID01 |
Number of CE (Check Engine) Codes |
PID03 |
PID03 |
CLL (Closed Loop Lambda) Status |
PID04 |
PID04 |
Load (Abs) (clamped to 0-100%) |
PID05 |
PID05 |
ECT (Engine Coolant Temperature) |
PID06 |
PID06 |
Short Term Fuel Trim - Bank 1 |
PID07 |
PID07 |
Long Term Fuel Trim - Bank 1 |
PID08 |
PID08 |
Short Term Fuel Trim - Bank 2 |
PID09 |
PID09 |
Long Term Fuel Trim - Bank 2 |
PID0A |
PID10 |
Fuel Rail Pressure (gauge) |
PID0B |
PID11 |
MAP (Manifold Absolute Pressure) |
PID0C |
PID12 |
Engine Speed |
PID0D |
PID13 |
Vehicle Speed |
PID0E |
PID14 |
Ignition Timing Advance for #1 Cylinder |
PID0F |
PID15 |
IAT (Intake Air Temperature) |
PID10 |
PID16 |
MAF |
PID11 |
PID17 |
Absolute Throttle Position |
PID13 |
PID19 |
Number of O2 sensors present (based on CLL banks) |
PID1F |
PID31 |
Engine Running Time |
PID22 |
PID34 |
Differential Fuel Rail Pressure |
PID23 |
PID35 |
DI Fuel Rail Pressure |
PID24 |
PID36 |
O2 Sensor 1 Equivalence Ratio |
PID25 |
PID37 |
O2 Sensor 2 Equivalence Ratio |
PID26 |
PID38 |
O2 Sensor 3 Equivalence Ratio |
PID27 |
PID39 |
O2 Sensor 4 Equivalence Ratio |
PID28 |
PID40 |
O2 Sensor 5 Equivalence Ratio |
PID29 |
PID41 |
O2 Sensor 6 Equivalence Ratio |
PID2A |
PID42 |
O2 Sensor 7 Equivalence Ratio |
PID2B |
PID43 |
O2 Sensor 8 Equivalence Ratio |
PID33 |
PID51 |
BAP (Barometric Pressure) |
PID42 |
PID66 |
Control Module Voltage |
PID44 |
PID68 |
Commanded Equivalence Ratio (Lambda Target) |
PID45 |
PID69 |
Relative Throttle Position |
PID47 |
PID71 |
Absolute Throttle Position B (TPS Sub) |
PID49 |
PID73 |
Absolute Pedal Position D (APS Main) |
PID4A |
PID74 |
Absolute Pedal Position E (APS Sub) |
PID4C |
PID76 |
Commanded Throttle Actuator Control (E-Throttle Target) |
PID52 |
PID82 |
Ethanol Fuel % |
PID59 |
PID89 |
Absolute Fuel Rail Pressure (Fuel Pressure + BAP) |
PID5A |
PID90 |
Relative accelerator pedal position (APS Main) |
PID5C |
PID92 |
Engine Oil Temperature |
PID5D |
PID93 |
Fuel Injection Timing |
PID5E |
PID94 |
Inst Fuel consumption (L/h) |


